A Mill Test Certificate (MTC), or Mill Test Report (MTR), is issued by a manufacturer to certify the chemical and mechanical features of a product and its compliance to the applicable norms and technical specifications. Typically, Mill Test Certificates conform to the EN 10204 standard and are related to steel products.
MILL TEST CERTIFICATE
A mill test certificate to EN 10204 shows, generally, the following information:
- Type of certificate and standard (example EN 10204 3.1 or EN 10204 3.2)
- Manufacturer name
- Product name and dimensions
- Quantity covered by the certificate (example: tons, with heat numbers)
- Heat numbers and batch number (physically shown on the product as well)
- Final test result
- Dimensional measurements, to check compliance with allowed tolerances (example, for steel pipes: diameter, wall thickness, length, straightness)
- Material grade and applicable specification, including results of chemical and mechanical tests
- Results of additional tests, like hydrostatic, ultrasounds (UT), hardness, impact test, magnetic particles, metal graphic result etc.
- Addenda useful to appraise the full features of the product
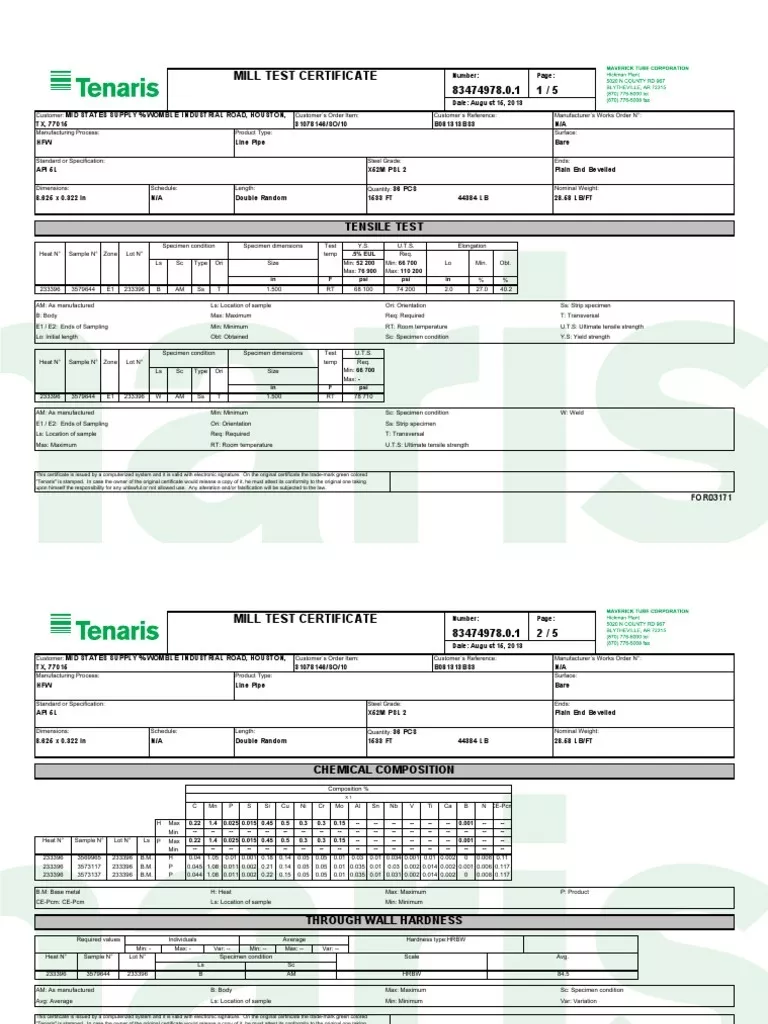
Sample mill test certificate (Tenaris steel pipes).
TYPES OF MILL TEST CERTIFICATE (EN 10204 2.1, 2.2, 3.1, 3.2)
| Mill Test Certificate denomination in… | |||||
| MTC Type EN 10204 | English | German | French | Scope | MTC to be validated by… |
| MTC Type 2.1 | Declaration of compliance with the order | Werk- Bescheinigung | Attestation de conformité á la Commande | Statement of compliance with the order | The manufacturer |
| MTC Type 2.2 | Test report | Werkzeugnisse | Relvé de contrôle | Statement of compliance with the order by the manufacturer based on non-specific inspections (tests) by the manufacturer. | The manufacturer |
| MTC Type 3.1 | Inspection certificate 3.1 | Abnahmeprüf- Zeugnisse 3.1 | Certificat de réception 3.1 | Statement of compliance with the order by the manufacturer with results of a specific inspection | The manufacturer`s authorized inspection representative, independent by the manufacturing department |
| MTC Type 3.2 | Inspection certificate 3.2 | Abnahmeprüf- zeugnisse 3.2 | Certificat de réception 3.2 | Statement of compliance with the order with an indication of results of a specific inspection |
|
EN 1024 3.1 MILL TEST CERTIFICATE
| Certificate type | Title | Summary of EN10204 requirements | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1 | Inspection certificate | Statement of compliance with the order by the manufacturer with results of specific inspection | Replaces 3.1B. Common certificate type issued for ‘batch tested’ material. Cert. issued and signed by the manufacturer’s representative, who must be independent of the manufacturing department. Eg Inspection department or test house manager/supervisor. |
| 3.1A | Inspection certificate 3.1A | With a mention of test results from specific inspection and testing | Batch test results. Cert. issued by independent inspector required by releasing authority (eg TUV for German pressure vessels). Replaced by 3.2 in 2004 |
| 3.1B | Inspection certificate 3.1B | With a mention of test results from specific inspection and testing | Batch test results. Cert. issued and signed by the manufacturer’s representative. Replaced by 3.1 in 2004 |
| 3.1C | Inspection certificate 3.1C | With a mention of test results from specific inspection and testing | Batch test results. Cert. issued by an independent inspector appointed by a customer (eg Lloyds). Replaced by 3.2 in 2004 |
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment